The purpose of this article is to define the words and terms used throughout these regulations. Words and terms that are specific to a particular article of these regulations may be defined in said article.
A. Any definition of a word or term provided in these regulations shall apply to each use of the word or term within these regulations, unless the context clearly indicates otherwise or the meaning or scope is expressly limited.
B. Words or terms used, but not defined in these regulations, shall have their ordinary meaning as defined in a reputable dictionary.
C. Drawings, diagrams or other illustrations may be provided to clarify the meaning, interpretation or application of certain definitions.
Accessory: A structure or use that is subordinate or incidental to the primary land use of a given property parcel. The following definitions are provided for specific related terms.
Accessory Apartment: An accessory residential unit that is constructed within or attached to the primary structure on a parcel or another accessory structure, such as a garage.
Accessory Dwelling: An accessory residential unit that is detached from the primary structure on a parcel.
Accessory Structure: A building or other structure that serves a function that is incidental to that of the primary structure on a parcel. Some typical examples include garages, carports and storage sheds.
Accessory Use: A land use or activity that is incidental to that of the primary use of a parcel. Some typical examples include parking areas, tennis courts, swimming pools, and home occupations.
Aircraft: A vehicle capable of flight, which may or may not carry passengers. Some typical examples include airplanes, helicopters, model aircraft and drones.
Alteration: The physical modification or reconfiguration of an existing or approved structure or its component parts. Some typical examples include room/garage additions (expand building footprint), floor additions (extend building height) and sign relocations.
Applicant: The property owner or other person with legal authorization to request approval for a building, structure or use governed by these regulations and whose signature must certify such authority on permit applications.
Basement: Any usable story of a structure with at least one-half (½) of its height below the adjacent finished grade.
Block: A contiguous tract of one or more parcels within a subdivision that has boundaries defined by streets, public parks, railroad rights-of-way, city limits, other property lines, easements or natural barriers, such as waterways.
Buildable Area: The area of a lot wherein allowable obstructions may exist or may be constructed.
Building: A covered and enclosed structure where activities associated with a primary, secondary or accessory land use take place. Buildings that are interconnected by covered and enclosed walkways, breezeways and similar structures are considered a single building. Buildings sharing a common wall, but having separate entrances are considered individual buildings.
Building Footprint: The area representing the perimeter of a structure at its foundation or point of vertical intersection with the adjacent finished grade.
Bulk Regulations: Requirements or provisions that control the size of a structure and its location on a parcel. Examples included in these regulations are maximum height, maximum lot coverage, minimum yard size and setbacks.
By-Right Use: A structure or use that is allowed within a specific zoning district because it is generally compatible with other uses allowed within the same zoning district. By-right uses must meet only the minimum zoning district requirements for the use, unless it is subject to specific use standards.
Canopy: A covered, but unenclosed accessory structure that provides shelter for individuals performing activities associated with the primary, secondary or accessory use of a parcel. Some typical examples include those found over a building entrance, drive-thru facility, fuel pumps or temporary parking spaces. This does not include structures meeting the definition of carport.
Carport: A covered accessory structure, which may be fully or partially unenclosed, intended to shelter motor vehicles parked in permanent parking spaces. Carports may be freestanding, but if attached to another structure, may only be attached to the primary building on a parcel.
Conditional Use: A structure or use that is not allowed by-right within a specific zoning district because of characteristics that are somewhat incompatible with other uses allowed in the same zoning district. A conditional use may be authorized according to the process and procedures defined in these regulations. Such authorization may be subject to additional provisions (conditions) intended to improve compatibility with other uses allowed in the zoning district.
Density: The degree to which individual properties are developed with structures, which dictates the overall distribution of a community’s structures and population. These regulations control density primarily through bulk and lot size requirements.
Condominium: A type of residential ownership wherein a single structure is divided into multiple individually owned dwelling units with common areas owned by a property owners association. Examples of common areas in condominium apartments are hallways, stairs/elevators, lawns, and parking lots. Garden home and townhome condominium developments have separate ownership of individual dwelling units with common ownership of individual lots and amenities such as clubhouses, pools, etc.
Develop: The act of making a tract of property suitable for a specific land use. Includes changing the physical characteristics of land in preparation for structures, utilities, streets and infrastructure or the construction of such improvements (development). Properties having such improvements are developed. Properties without such improvements are undeveloped or vacant. The individual or entity making such improvements is referred to as the developer.
Disability: A physical or mental impairment that substantially limits a person’s major life activities or a record of having such an impairment.
District (Zoning): A section or sections of the zoning jurisdiction within which these regulations govern the use of buildings and land, the height of buildings, the size of yards, and the intensity of uses in a uniform manner.
Driveway: A private roadway providing access to a parking space.
Dwelling: A structure designed and used primarily for residential purposes. Each portion of a dwelling specifically intended as an individual residence for one (1) family or household is considered a dwelling unit. Secondary uses and activities, such as allowable home occupations, may also take place within a dwelling unit.
Easement: A legal instrument wherein a landowner grants permanent or temporary use rights for a defined property to another person or legal entity, but retains title and ownership of said property.
Family: One (1) or more individuals living together in the same dwelling unit as a single household.
Fence: A free-standing structure that meets the provisions of these regulations and serves as a protective, confining or decorative barrier between adjacent lots or uses.
Frontage: The length of distance along a lot line that abuts and is shared in common with a public street.
Garage: A covered and enclosed accessory structure that provides direct access to a driveway or parking space, which is intended solely for storage of motor vehicles owned by residents of the primary structure. A garage may be attached to or detached from a primary residential structure.
Gross Floor Area: The unit of measurement for the space within a structure as measured between the exterior faces of exterior walls or centerlines of shared common walls on each story (floor) of a structure. Includes basements and attics having headroom of seven (7) feet or more.
Height (Structure): A vertical dimension measured from the finished lot grade at the front of a structure to the highest point on the structure. For buildings and other covered structures, this is measured to the highest point of the roof. For signs, towers and other uncovered structures, this is measured to the highest point of the structure itself or of anything attached to the structure, whichever is greater.
Home Occupation: A business, profession, service or trade allowed by these regulations to be conducted for gain or support entirely within the primary residence of the business owner. Activities related to a home occupation are restricted from occurring in a secondary or accessory structure, except as allowed by these regulations.
House Pet: A legally-owned domesticated small animal routinely kept as a family pet and generally housed within the primary residential structure. Some typical examples include dogs, cats, birds, hamsters and aquarium fish.
Intensity: The degree of activity generated by a specific land use and the potential impacts those activities have on surrounding properties. The hierarchy of zoning districts is based on the intensity of land uses allowed within each district.
Landscaping: Plants, trees, yard art and other improvements generally intended to beautify a property.
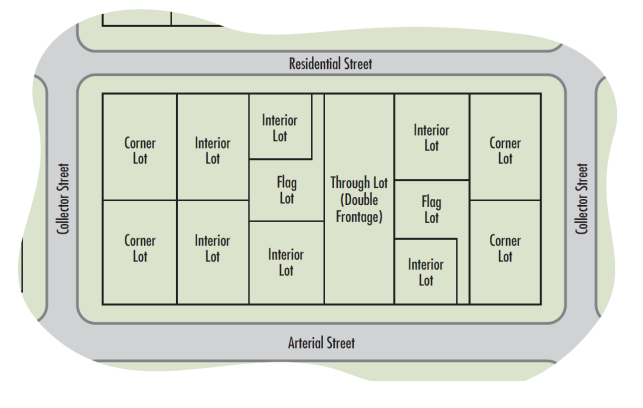
Lot of Record: An individual parcel of land under single ownership that has a legal description and deed recorded with the Butler County Register of Deeds. Various types of lots are defined below and illustrated in Figure 3.1.
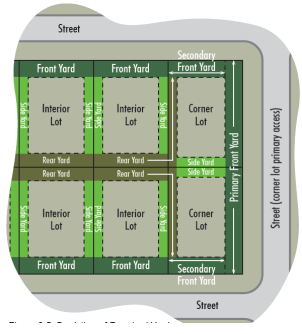
Corner Lot: A lot with frontage on two or more intersecting streets.
Flag Lot: A lot shaped like a flag that has street frontage significantly narrower than its main portion, which is typically where the driveway is located.
Interior Lot: A lot other than a corner lot that has frontage on only one street.
Through (Double Frontage) Lot: A lot with frontage on two non-intersecting street.
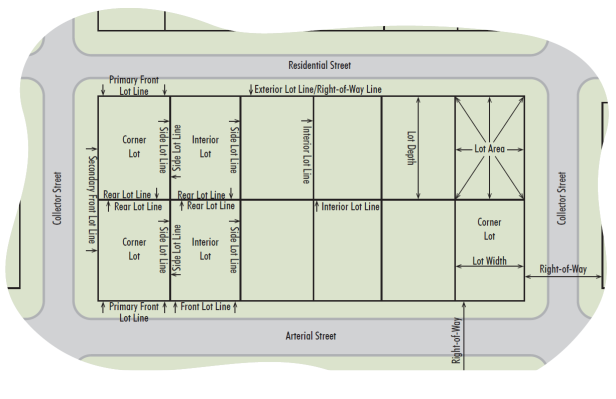
Lot Line: A legal boundary of a lot of record. See Figure 3.2.
Front (interior lot): The lot line with street frontage. May also be referred to as the street line.
Front (corner lot): The lot line along the primary access street, typically the street to which the address is assigned.
Rear: The lot line that is most distant from and generally parallel to the front lot line (primary front lot line on a corner lot).
Side: A lot line that is not a front or rear lot line.
Exterior: A rear or front lot line that is not shared by another lot of record, which typically marks the boundary of a block, right-of-way or natural barrier.
Interior: A rear or side lot line shared by two or more lots of record.
Lot Size Requirements: Restrictions on the dimensions of a lot. See Figure 3.2.
Lot Area: The surface measurement encompassed by a lot’s boundaries.
Lot Depth: The dimension between the front and rear lot lines, as measured from their midpoints.
Lot Width: For an interior lot, the dimension between side lot lines as measured along the front yard setback line. For a corner lot, the dimension between the secondary front lot line and side lot line as measured along the primary front yard setback line.
Nonconforming: A lot, structure, sign or land use within the City zoning jurisdiction that does not meet the applicable provisions of these regulations. Such is considered legal nonconforming if it existed lawfully prior to the adoption of these regulations, which is commonly referred to as being “grandfathered.”
Obstruction: Any encroachment within a required setback area (yard), sight triangle or other area where such restrictions are indicated in these regulations.
Permanent: A term referring to a use, structure or activity that is intended to remain in place or be conducted in perpetuity with no limit on its duration.
Premise(s): The land, building and structures located on a lot.
Primary (or Principal) Structure: The structure in which the main activities of a primary use take place. Primary (or Principal) Use: The main purpose for which a lot of record is used and developed.
Recreational Vehicle (RV): A legally licensed, appropriately registered, and operable single-chassis vehicle or trailer designed as a temporary lodging unit for travel or camping; a trailer-mounted “tiny home.”
Right-of-Way: Real property that is dedicated to a public entity for current or future transportation, utility or other infrastructure uses, including the area on, below, and above such property. See Figure 3.2.
Screening: A man-made or natural barrier used to minimize the visual impact of a property from outside its perimeter or minimize the effects of noise, dust or other impacts that may be generated on the site.
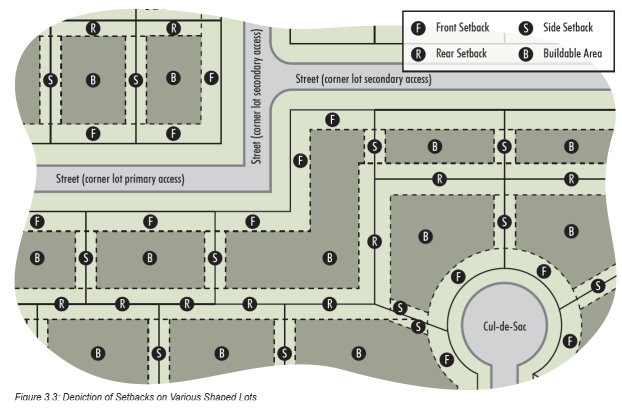
Setback: The required minimum distance between a structure and a front, side or rear lot line of the lot on which it is located. These are considered the front, side and rear setback lines respectively. The space between all setback lines is referred to as the buildable area. See Figure 3.3.
Sight Triangle: The area at a street’s intersection with another street, alley or driveway that must be kept clear from obstructions that may block a driver’s line of sight to oncoming traffic. See Section 04.06.L.
Street: A public right-of-way intended to carry vehicular, pedestrian and bicycle traffic.
Alley: A minor right-of-way intended to provide secondary access to property parcels.
Local Street: A low volume street that functions mainly to provide direct access to property parcels.
Collector Street: A street that carries traffic between local and arterial streets, which has some direct access to property parcels.
Arterial Street: A street that carries traffic through and out of a community, which has limited direct access to property parcels.
Structure: Anything constructed that is permanently attached to the ground or affixed to a permanent location on the ground that is subject to these regulations, unless otherwise exempted.
Subdivision: A contiguous tract of land made up of one or more parcels that has been divided into individual lots intended for separate ownership. Subdivisions are broken into additions, blocks and lots, which are used to identify the properties by a legal description. This hierarchy of divisions is illustrated on a map, referred to as a “plat,” which is filed of record with the county Register of Deeds. The subdivision of land in Augusta is governed by the City of Augusta Subdivision Regulations.
Temporary: A term referring to a use, structure or activity that is not intended to remain in place or be conducted in perpetuity. Such may be allowed or permitted for a specific duration with a set time limit.
Use: The purpose for which a lot of record is developed or proposed to be developed. This generally describes the types of human activities that occur or will occur on the subject property.
Utility Pole: A structure owned or operated by a public utility as defined in K.S.A. 66-104, and amendments thereto, a municipality as defined in K.S.A. 75-6102, and amendments thereto, or an electric cooperative as defined in K.S.A. 2015 Supp. 17-4652, and amendments thereto, that is designed specifically for and used to carry lines, cables, or wires for telecommunications, cable, electricity, or to provide lighting.
Utility Trailer: A trailer (loaded or unloaded) with multiple axles or having a bed length that exceeds ten (10) feet that is designed to haul vehicles, watercraft, work equipment, or animals; or used for general utility purposes.
Variance: An approval granted by the Board of Zoning Appeals consistent with Section 15.05, which allows for deviations from one or more requirements of these regulations.
Wind Energy Conversion Systems: Equipment that converts and transfers energy from the wind into usable forms of electrical energy.
Wireless Communications: Personal wireless services and facilities defined by 47 USC § 332(c)(7)(C), including commercial mobile services defined by 47 USC § 332(d), provided to personal mobile communication devices through wireless facilities or any wireless services provided using such facilities. As used herein, the term applies specifically to the services and facilities defined in and regulated by K.S.A. 17-1902 et seq. This includes the following related terms.
Accessory Equipment: Apparatus serving or being used in conjunction with a wireless facility or wireless support structure including, but not limited to utility or transmission equipment; power supplies; generators; batteries; cables; equipment buildings and cabinets; and storage sheds, shelters or similar structures.
Antenna: Equipment that transmits or receives electromagnetic radio signals used in the provision of wireless communications services.
Base Station: A structure that supports or houses an antenna, transceiver, coaxial cables, power cables or other associated equipment at a specific site that is authorized to communicate with mobile stations.
Collocation: The mounting or installation of wireless facilities on a building, structure, wireless support structure, tower, utility pole, base station or existing structure for the purposes of transmitting or receiving radio frequency signals for communication purposes.
Distributed Antenna System: A network that distributes radio frequency signals and consisting of: 1) remote communications or antenna nodes deployed throughout a desired coverage area, each including at least one antenna for transmission and reception; 2) a high capacity signal transport medium that is connected to a central communications hub site; and 3) radio transceivers located at the hub’s site to process or control the communications signals transmitted and received through the antennas to provide wireless or mobile service within a geographic area or structure.
Lattice Tower: A type of support structure that consists of an open network of braces forming a tower that is usually triangular or square in cross section.
Modification and/or Replacement: Modification of a support structure or wireless communication facility of comparable proportions and of comparable height or such other height that would not constitute a substantial modification in order to support wireless facilities or to accommodate collocation and includes replacement of any pre-existing wireless communication facility or support structure.
Monopole: A type of support structure that consists of a vertical pole fixed into the ground and/or attached to a foundation.
Small Cell Facility: A wireless communication facility that meets both of the following qualifications: 1) each antenna is located inside an enclosure of no more than six cubic feet in volume, or in the case of an antenna that has exposed elements, the antenna and all of the antenna’s exposed elements is no more than three cubic feet; and 2) primary equipment enclosures that are no larger than 28 cubic feet in volume, or facilities comprised of such higher limits as the federal communications commission has excluded from review pursuant to 54 U.S.C. § 306108. Associated equipment may be located outside the primary equipment, and if so located, is not to be included in the calculation of equipment volume. Associated equipment includes, but is not limited to, any electric meter, concealment, telecommunications demarcation box, ground-based enclosures, back-up power systems, grounding equipment, power transfer switch, cut-off switch, and vertical cable runs for the connection of power and other services.
Substantial Modification: Any change to a wireless communication facility or support structure that will substantially change the physical dimensions under the objective standard for substantial change, established by the Federal Communications Commission pursuant to 47 CFR 1.40001.
Transmission Equipment: Apparatus that facilitates transmission for a wireless service licensed or authorized by the Federal Communications Commission including, but not limited to radio transceivers, antennas, coaxial or fiber optic cable and regular and backup power supply.
Wireless Facility: Equipment at a fixed location that enables wireless communications between user equipment and a communications network.
Wireless Facility Support Structure: A freestanding structure, such as a monopole, guyed or self-supporting tower or other suitable existing or alternative structure designed to support or capable of supporting wireless facilities, and any structure that is currently supporting or designed to support the attachment of wireless facilities, including, but not limited to, towers, buildings, and water towers. See Figure 3.4.
Wireless Infrastructure Provider: A person or entity that builds or installs transmission equipment, wireless facilities or wireless support structures, but is not a wireless services provider.
Wireless Services Provider: An entity that provides wireless services.

Yard: The open space on a lot within which only permitted obstructions are allowed. See Figure 3.5.
Front Yard: The required yard extending the full width of a lot, as measured between the front lot line and front setback line. On a corner lot, both yards abutting a street are considered front yards. May also be referred to as the street yard.
Rear Yard: The required yard extending the full width of a lot, as measured between the rear lot line and the rear setback line. On a corner lot, any yard not considered a side or front yard is a rear yard.
Side Yard: The required yard extending the depth of a lot between the front and rear setback lines. On a corner lot, any yard abutting the side yard of an adjacent property is considered a side yard.
Zero Lot Line (ZLL): The location of a building on a lot such that: (A) one or more exterior walls of a detached unit rest directly on an interior lot line, or (B) the shared common wall of two attached units rests on an interior lot line. Some typical examples are patio homes, garden homes, and condominium townhomes.
Zoning Compliance Certificate: A document issued by the Zoning Administrator, which states that a given property is appropriately zoned and meets all applicable provisions of these regulations for: (A) establishing a specific use; (B) changing an established use; (C) constructing, altering, or modifying a structure; or (D) establishing occupancy in an existing structure previously occupied with a different type of use.
Zoning Jurisdiction: The geographic boundaries wherein the City has the legal authority to adopt and enforce zoning regulations. This is the City of Augusta corporate limits.
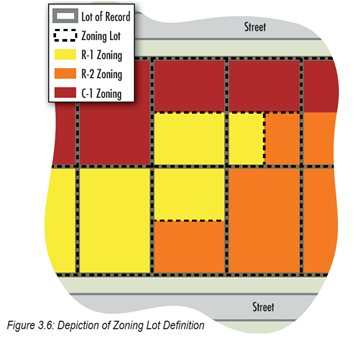
Zoning Lot: A contiguous area of property on one or more lots of record having the same owner, the entire area of which is within the same zoning district. Where a single lot of record has portions within different zoning districts, each portion within a different zoning district is considered an individual zoning lot. See Figure 3.6.